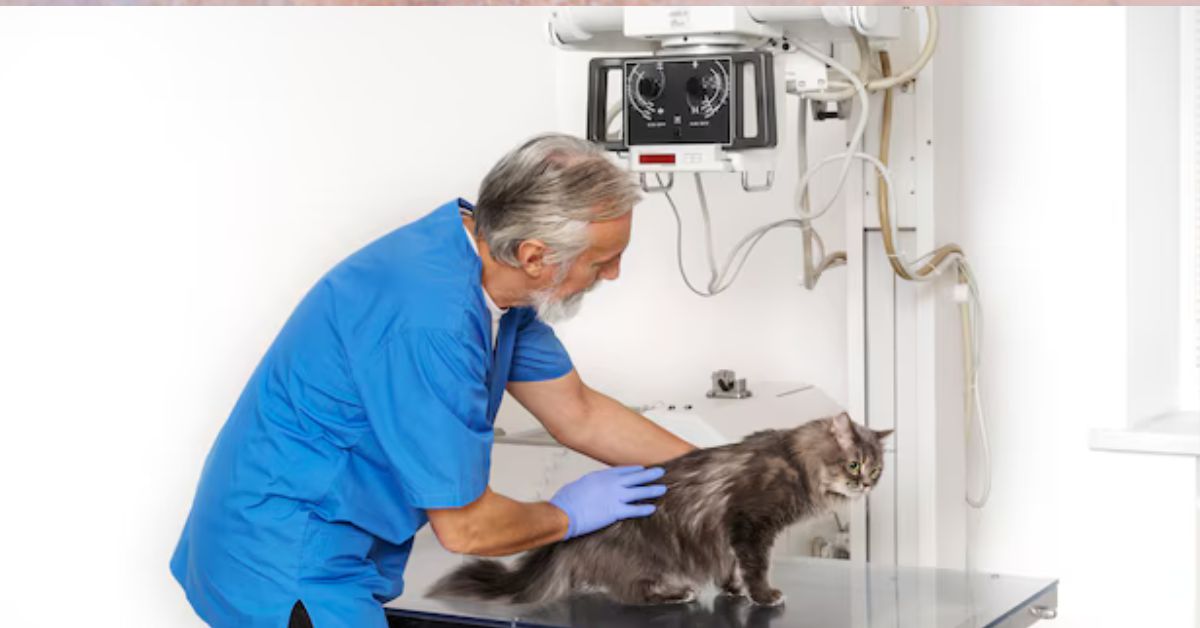
In veterinary medicine, cat imaging has become a vital technology that provides deep insights into the health and welfare of our feline friends. Cat imaging is crucial for making precise diagnoses and enhancing results, whether it is used to look at an accident, track the effectiveness of a treatment, or detect a possible sickness. This article explores cat imaging methods in detail, emphasizing the value of these technologies, their different varieties, and their uses in contemporary veterinary care.
Upon finishing this article, you will have a better understanding of the many imaging techniques used for cats, their components, and how veterinarians use these tools to make well-informed judgments about your pet’s health.
Cat Imaging: What Is It?
The different methods used to view a cat’s internal anatomy for diagnostic reasons are collectively referred to as “cat imaging.” Similar to human medicine, imaging is essential for detecting health issues that would be difficult to find with just physical exams. By assisting vets in evaluating organs, tissues, and bones, it helps them identify illnesses and injuries early on, which can greatly enhance the effectiveness of treatment.
The following imaging methods are most frequently employed in cat veterinary medicine:
1. Radiography, or X-rays
2. Ultrasonic
3. Computed Tomography (CT) scans
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI
5. Endoscopy
Making the best diagnostic choices for cats requires an awareness of the differences between these techniques, each of which has special benefits for diagnosing various ailments.
Cat Imaging Technique Types
1. Radiography, or X-rays
One of the most often utilized methods in veterinary diagnostics is X-ray imaging, which is frequently the first thing a veterinarian does when they suspect a cat’s body of having malignancies, bone fractures, or foreign items. X-rays produce images of the cat’s internal structures using electromagnetic radiation.
X-rays can be used to diagnose bone anomalies, fractures, and dislocations in cats.
• Determining whether growths, infections, or malignancies are present.
• Finding foreign objects in the intestines or stomach.
• Keeping an eye on respiratory disorders like heart failure or pneumonia.
Even though X-rays are very helpful, their 2D image might not fully depict the intricacies of inside anatomy, particularly for organs like the brain, liver, or kidneys.
2. Ultrasonic
High-frequency sound waves are used in ultrasound imaging to produce live images of the inside organs and tissues. Ultrasound is a safer alternative to X-rays because it doesn’t use radiation, especially for repeat imaging.
Ultrasound is used in cats for the following purposes: • Assessing soft tissues such the heart, liver, kidneys, and bladder.
• Evaluating the health of the fetus and the pregnant cat.
• Directing fluid drainage or biopsies.
• Recognizing problems such as organ enlargement, abscesses, or cysts.
In areas that X-rays cannot clearly detect, such as tissue density, fluid accumulation, and organ function, ultrasound is especially useful.
3. Computed Tomography (CT) scans
A CT scan creates cross-sectional images, or slices, of the body by processing a sequence of X-ray pictures obtained from various perspectives. Veterinarians can use this technique to look closely at interior tissues, which is particularly useful for identifying illnesses or injuries in places that are hard to evaluate with conventional X-rays.
CT scan applications in cats:
• A thorough analysis of the blood vessels, soft tissues, and bones.
• Finding anomalies, infections, or malignant tumors in intricate areas like the brain or spine.
• Recognizing brain disorders including bleeding or tumors.
Because of its accuracy, CT scans are very helpful in identifying illnesses that need a high level of information or in surgical planning. They provide detailed 3D images.
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI
MRI is one of the most sophisticated imaging methods for identifying neurological or muscular conditions in cats because it creates fine-grained images of soft tissues using powerful magnetic fields and radio waves. MRIs are a safer option for soft tissue imaging because they don’t use ionizing radiation.
MRI applications in cats include:
• Examining neurological problems, spinal cord disorders, and brain disorders.
• Making the diagnosis of muscle or joint issues, such as soft tissue injuries or torn ligaments.
• Finding anomalies or cancers in soft tissues and organs.
Compared to CT scans or X-rays, MRI imaging offers improved contrast, making it possible to distinguish soft tissues more clearly.
5. Endoscopy
Using a flexible tube with a camera attached, endoscopy is a minimally invasive treatment that enables veterinarians to see into a cat’s body. This method is frequently employed to investigate regions that are challenging to access using other imaging techniques.
Endoscopy can be used to visualize the respiratory, urinary, or gastrointestinal tracts in cats.
Removing foreign things from the intestines or stomach; taking samples of tissues or foreign bodies for additional analysis.
The benefit of endoscopy is that it can identify and treat certain issues without the need for surgery.
Comparison of Cat Imaging Techniques
| Imaging Technique | Pros | Cons | Best For |
| X-rays | Quick, inexpensive, ideal for bone fractures | Limited soft tissue visibility, 2D images | Bone fractures, lung conditions, foreign objects |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, safe, no radiation, real-time imaging | Limited by operator skill, not ideal for bones | Soft tissue issues, pregnancy, fluid buildup |
| CT Scans | Detailed 3D images, excellent for complex cases | Expensive, requires anesthesia, uses X-rays | Brain conditions, complex fractures, tumors |
| MRI | Excellent for soft tissues, no radiation | Expensive, requires anesthesia, longer procedure | Neurological disorders, joint and muscle issues |
| Endoscopy | Minimally invasive, provides direct visualization | Limited to specific areas, requires sedation | GI tract, respiratory issues, foreign body removal |
The Significance of Cat Imaging for Pet Health
Imaging is essential to raising the standard of veterinary care. Here’s how:
1. Early Identification
The likelihood that a problem will be successfully treated increases with early diagnosis. Many illnesses, like heart disease or cancer, could not manifest symptoms until they are extremely advanced. Early detection of these problems by imaging can help avoid major complications.
2. Correct Treatment Scheduling
Imaging helps vets choose the best course of treatment after a diagnosis has been determined. A thorough picture of the affected area guarantees the best potential outcome from any treatment, be it physical therapy, medicine, or surgery.
3. Reducing invasive operations
Veterinarians can perform non-invasive evaluations of a cat’s health with the aid of imaging. As a result, there will be fewer needless or exploratory surgeries. For example, a biopsy can be guided by ultrasonography, negating the need for extensive surgical examination.
4. Tracking Development
Imaging aids in monitoring the healing process after therapy. Frequent follow-up scans, such MRIs or X-rays, make sure that therapies are working and that a condition isn’t getting worse.
How to Get Your Cat Ready for Pictures
The method employed determines how to prepare for imaging. Here is a broad summary:
1. For X-rays and CT scans: Your cat may require sedation for X-rays and CT scans, particularly if it is nervous or has to stay still. There may be a fasting period necessary for some scans.
2:For Ultrasound: Your cat must be calm during the ultrasound, and in certain situations, the fur in the examined area may need to be shaved.
3. For MRI: Your cat will need to fast before the test, and your veterinarian will give you detailed instructions because MRIs frequently call for sedation.
Cat Imaging’s Future
Veterinary imaging is still a developing field. More sophisticated imaging methods that are improved by artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze images more precisely and effectively may be developed in the future. AI has the potential to improve treatment outcomes by detecting small changes in images, which could lead to early diagnosis of diseases like cancer.
Furthermore, a wider range of veterinary practices may be able to use these techniques thanks to portable and more reasonably priced imaging equipment, guaranteeing that more cats receive prompt diagnoses and treatments.
In conclusion
A crucial component of contemporary veterinary care is cat imaging. It offers vital information about a cat’s health, enabling prompt identification, precise diagnosis, and efficient treatment regimens. Every technology, from the well-known X-ray to more sophisticated ones like MRI and CT scans, offers advantages and is appropriate for a particular diagnostic requirement.
Imaging will play an increasingly important role in feline health as veterinary technology advances, ensuring that cats continue to live longer, healthier lives. Knowing cat imaging enables you to make better decisions for your feline friends’ health, whether you’re a veterinarian or a worried cat owner.