Virtual reality (VR) has quickly developed into a game-changing technology that is transforming a number of sectors, including gaming, entertainment, education, and healthcare. VR technology’s potential uses grow as it develops further, giving consumers and companies new ways to interact with the virtual world. The benefits, drawbacks, and industries where virtual reality (VR) is having the biggest influence are all examined in this article.
Virtual reality (VR): what is it?
A simulated experience that immerses people in a three-dimensional, interactive environment through computer-generated visuals, sounds, and other sensations is known as virtual reality (VR). In order to enable users to interact with the virtual world in a realistic manner, VR technology usually necessitates the employment of specialized hardware, such as gloves, motion sensors, and VR headsets.
In contrast to traditional media, which merely displays content for viewing, virtual reality (VR) produces an entirely immersive experience that frequently fools the brain into thinking the virtual world is real. VR is being used for creative solutions in a variety of industries, including healthcare, education, real estate, and training programs. Its uses extend well beyond video games.
Virtual Reality’s (VR) Evolution
Although virtual reality (VR) has been around since the 1960s, the technology has only just started to advance. The first commercial VR systems, such Sega’s VR headgear and Nintendo’s Virtual Boy, were introduced in the 1990s. VR experiences were less than convincing because to these early attempts’ technical shortcomings, which included low-resolution screens and little interaction.
In the twenty-first century, virtual reality technology has advanced significantly. Experiences are now more realistic and immersive thanks to developments in tracking technology, computing power, and visuals. VR is now accessible to consumers because to the release of reasonably priced and easy-to-use headsets like the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR. Businesses have already started implementing VR in their operations for marketing, design, and training.
The Operation of Virtual Reality (VR)
Fundamentally, VR creates an interactive virtual world using a combination of hardware and software. Below is a summary of the essential elements that enable virtual reality to function:
1. Headsets: The most crucial piece of equipment for giving the consumer a visual experience are virtual reality headsets. High-resolution screens and lenses are used in well-known models such as the Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive Pro, and PlayStation VR to produce an authentic 3D experience.
2. Gloves and controllers: These tools let users engage with the virtual environment. Motion tracking and object manipulation in the environment are two frequent uses for controllers. Haptic feedback is another feature that some systems use to mimic touch.
3. Tracking Sensors: These sensors, which are frequently positioned around the surroundings or integrated into the headset, monitor the user’s head, hands, and body motions to enable smooth interaction with the virtual world.
4.Audio: For immersion, realistic sound is essential. In order to improve the overall experience, VR systems frequently employ 3D audio technology to place sounds in three dimensions.
5. Software: The virtual environment is powered by VR software. The software produces the interactive worlds and experiences that consumers interact with in video games and simulations.
Uses for Virtual Reality (VR)
VR has several uses outside of entertainment, even though it is most frequently linked to gaming. Here are a few of the major sectors and domains where virtual reality is having an impact.
1. Entertainment and Gaming
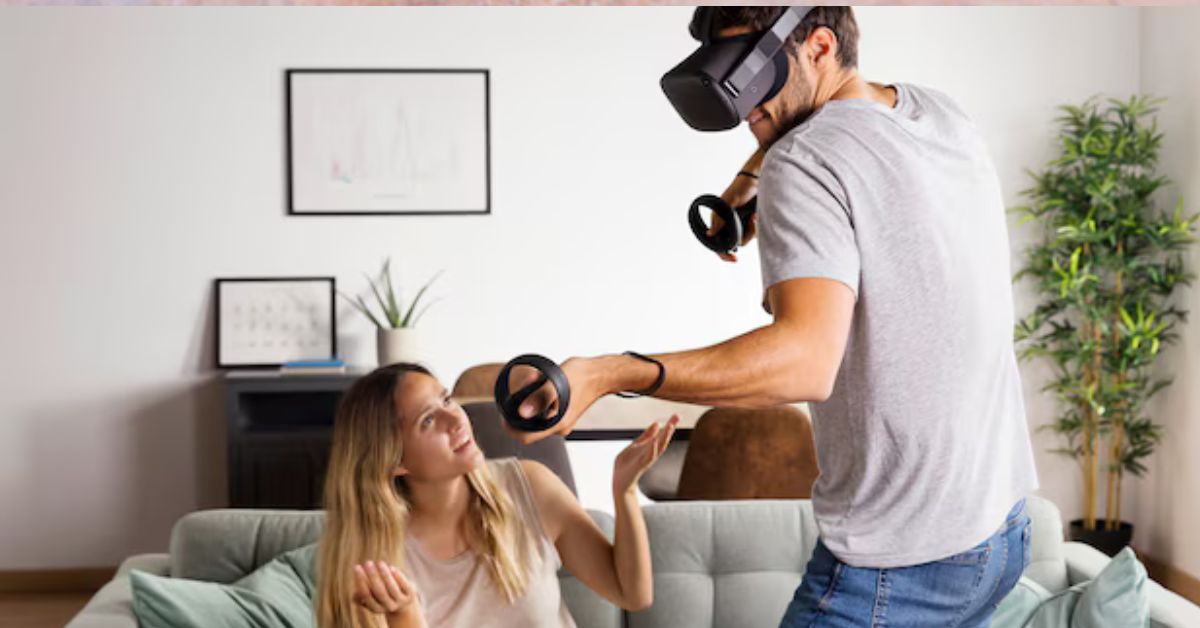
The main force behind the adoption of VR has been the game sector. The potential for immersive virtual reality experiences has been shown by games like Beat Saber and Half-Life: Alyx, where users can interact with the game world using motion controls and spatial awareness. Virtual reality (VR) gives players a sense of presence in the game environment and delivers a level of interaction and immersion that traditional gaming cannot equal.
VR is gaining traction in the entertainment and film sectors in addition to gaming. A fascinating new frontier is virtual reality cinema, which allows audiences to experience movies from inside the narrative. In contrast to conventional flat-screen media, a number of virtual reality films and experiences let viewers wander and gaze about, making for a more captivating viewing experience.
2. Medical Care and Treatment
Virtual reality is being used in healthcare for everything from medical teaching to pain management. While patients use virtual reality (VR) to relieve pain or anxiety, surgeons use it to perform intricate procedures in a risk-free setting. VR experiences, for instance, have helped patients receiving chemotherapy by diverting their attention from the agony of the procedure.
Virtual reality (VR) is being utilized in physical therapy, where patients can complete exercises in a safe, virtual setting. Compared to conventional techniques, virtual reality (VR) can assist patients improve their mobility and coordination by giving them real-time feedback.
3. Instruction and Practice
Because of its immersive qualities, virtual reality is a perfect tool for training and teaching. VR gives pupils the opportunity to investigate new ideas in a practical, participatory manner through field trips and virtual classrooms. While history students can “visit” past civilizations through VR-powered field trips, medical students can utilize VR to conduct virtual dissections.
VR is also being used by corporate training programs to enhance abilities. To lower the chance of mistakes and mishaps, workers might rehearse challenging or hazardous jobs in a virtual setting before carrying them out in real life.
4. Architecture and Real Estate
Virtual reality is revolutionizing the design, sale, and purchase of real estate and architecture. Without physically seeing the property, prospective buyers can use virtual tours to view homes from any location in the world. VR is a technology that architects may use to more immersively exhibit and alter their designs. Before construction ever starts, clients can “walk through” a building or space to have a better idea of the finished outcome.
5. Marketing and Retail
In order to give customers distinctive shopping experiences, retailers are integrating virtual reality (VR) into their marketing campaigns. Customers may explore and interact with products in virtual showrooms and businesses from the comfort of their homes, and VR ads provide more dynamic and captivating campaigns.
Virtual Reality’s Advantages (VR)
Virtual reality (VR) has several benefits in a variety of industries. Here are a few of the main advantages:• Increased Immersion: Virtual reality provides an unmatched level of immersion, giving users the impression that they are physically present in the digital environment. This enhanced awareness of presence is essential for training, treatment, and gaming applications.
• Better Training and Learning: Virtual reality (VR) improves training and learning by offering interactive and hands-on experiences. Compared to traditional methods, simulations and role-playing exercises are more engaging and aid in improving memory retention.
• Cost-Effective Training: Virtual reality (VR) eliminates the need for costly physical resources and the possibility of injury while training staff on challenging or hazardous activities. Additionally, it can offer chances for continuing education without requiring travel.
• Accessibility: People who might not normally be able to experience certain things can now do so thanks to virtual reality. For instance, people with limited mobility can go to virtual places they would
Limitations and Difficulties with Virtual Reality (VR)
Even with all of its advantages, virtual reality (VR) still has a number of drawbacks and restrictions.
• Expensive: VR gear, including as controllers, sensors, and headsets, can be pricey. Even if prices have come down over time, many users still cannot afford high-quality VR systems.
• Motion Sickness: When using virtual reality, some people feel uneasy or suffer from motion sickness, particularly in hectic settings. Although developers are making efforts to reduce these problems, it is still difficult.
Why Limited material: Despite its growth, VR material is still insignificant when compared to the abundance of traditional media. Its appeal may be limited by the dearth of varied VR experiences, especially for specialized audiences.
• Technical Barriers: Although VR technology has advanced significantly, there are still technical problems that might disrupt the immersion, such as latency, low-resolution screens, or inadequate processing power.
Virtual Reality’s (VR) Future
VR technology’s potential uses will only grow as it develops further. We may anticipate advancements in both software and hardware, including more complex, interactive virtual environments and smaller, more comfortable headsets. As artificial intelligence (AI) advances, virtual reality (VR) may also become more intuitive, providing individualized experiences according to user preferences and actions.
Long-term, even more immersive and linked experiences may result from VR’s convergence with other cutting-edge technologies like augmented reality (AR) and 5G. For example, 5G networks could allow more smooth and real-time VR interactions globally, or VR and AR could combine to create hybrid experiences.
Virtual Reality (VR) Comparison Chart
| Feature | Oculus Quest 2 | HTC Vive Pro | PlayStation VR | Valve Index |
| Price | $299 | $799 | $399 | $999 |
| Display Resolution | 1832 x 1920 per eye | 1440 x 1600 per eye | 960 x 1080 per eye | 1440 x 1600 per eye |
| Tracking | Inside-out tracking | External base stations | External camera tracking | External base stations |
| Field of View | 90° | 110° | 100° | 130° |
| Controllers | Touch controllers | Vive controllers | PlayStation Move | Knuckles controllers |
| Compatibility | Standalone or PC | PC-only | PlayStation 4/5 | PC-only |
| Audio | Built-in speakers | External headphones | Built-in speakers | External headphones |
| Comfort | Moderate | Excellent | Moderate | Excellent |
Conclusion
Virtual reality (VR) has the potential to further transform a number of sectors by offering users engaging and immersive experiences that were previously unthinkable. VR is not only a new technology but also a potent instrument for innovation in a variety of fields, including gaming, healthcare, education, and real estate. VR is a fascinating technology to follow in the upcoming years because we may anticipate even more possibilities as technology develops.